Protective relays are on a hair trigger as they constantly look at the three-phase electric power system and try to decide whether the system is normal, or under fault conditions. If they detect a fault, they will attempt to isolate that fault from the rest of the electrical system.
Electro-mechanical relays use magnets and mechanisms to look for specific problems on the three-phase power system, and each relay model should have identical functions and wiring. This allows relay testers to follow a script that creates the specific criteria required to make the mechanisms move, and prove that that specific function is operating correctly. Relay testers do not need to understand the three-phase power system when testing this generation of relays because the relays are identical and perform simple functions.
Modern digital relays can be extremely complex with interactions between elements and endless logic configurations. This means that two identical relay models can have completely different functions. While it is possible to carry the electro-mechanical testing philosophy into the digital realm by re-programming the relay when testing each element, this style of testing will not prove that the relay will operate when required. A relay tester who understands the three-phase electrical system can build test plans that test the entire relay, instead of individual pieces of it, to make sure the relay operates when required. These procedures can also be more effective and efficient than traditional test procedures.
We will cover the following topics in this lesson to give you a foundation in three-phase electrical theory to help you become a better relay tester:
Introduction to Electrical Fundamentals and Frequency
- How electricity is created
- What is a cycle
- How to count cycles
- Understand how frequency and cycles are related
- Converting cycles to seconds
- Converting seconds to cycles
- Converting cycles to cycles
Three-Phase Electric Power Systems
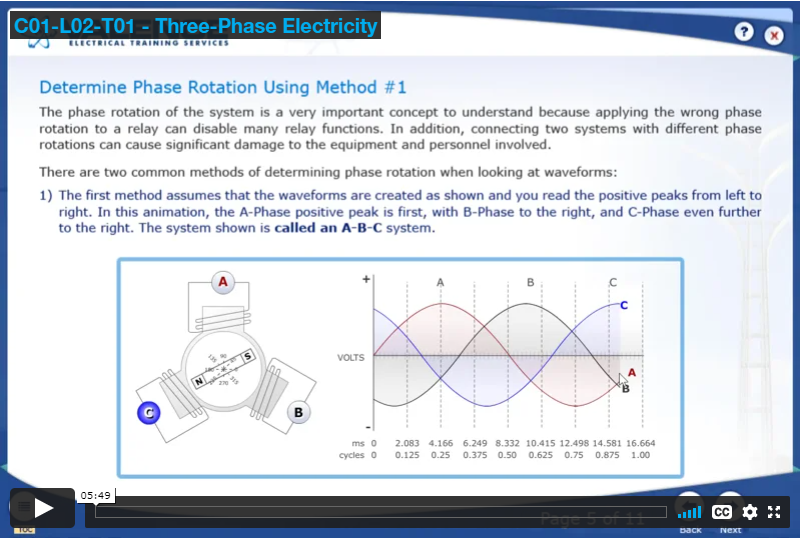
- How three-phase electric power systems are created
- How to determine what kind of three-phase electric power system is being generated
- How to change one kind of three-phase electric power into another
This course is eligible for 4 NETA Continuing Technical Development Credits (CTDs). NETA Certified Technicians (Level III and Level IV) are required to earn a minimum of 48 CTDs every three years to maintain their certification. For more information about the CTD program and requirements, please contact the NETA office at [email protected] or 888-300-6382.
What You Need to Take the Course
Most of the course content uses the Vimeo streaming video service, which is the equivalent of YouTube (without the ads, of course). You need a good internet connection, a computing device that can stream video, and some privacy (or headphones) to watch the videos. You can make all videos full screen by clicking the “Enter Full Screen Icon” ![]() on the bottom right hand side of the controls.
on the bottom right hand side of the controls.
Lesson 1-1-1: Electrical Fundamentals for Relay Testing
- Course 1-1: Pre-Quiz
- The Relay Testing Handbook: Electrical Fundamentals for Relay Testing
- Basic Electricity Video
- Counting Cyles
- Why Counting Cycles is an Important Skill to Know - Part 1
- Why Counting Cycles is an Important Skill to Know - Part 2
- Why Counting Cycles is an Important Skill to Know - Part 3
- Understanding Frequency and Cycles
- Why Understanding Frequency and Cycles is Important
- How to Convert Seconds to Cycles Sample Exercise
- How to Convert Seconds to Cycles Practice Questions
- How to Convert Cycles to Seconds Sample Exercise
- How to Convert Cycles to Seconds Practice Questions
- Converting Cycles-to-Seconds and Seconds-to-Cycles with Different References Sample Exercise #1
- Converting Cycles-to-Seconds and Seconds-to-Cycles with Different References Practice Questions #1
- Converting Cycles-to-Seconds and Seconds-to-Cycles with Different References Sample Exercise #2
- Converting Cycles-to-Seconds and Seconds-to-Cycles with Different References Practice Questions #2
- What Reference Does Your Relay or Test-Set Use
- Alternatives for More Information